Certificate of origin (CO): what is it and why is it needed?
A certificate of origin (CO) is a document that certifies the country in which a commodity or good was manufactured. This document is used in international trade to determine the source of the product and contains information such as the product description, value, and country of origin. The certificate of origin is used by customs authorities to determine the eligibility of goods for preferential tariff treatment and verify the authenticity of the goods being imported. Certificates of origin can also be used to enforce policy measures, like trade embargoes, import quotas, anti-dumping measures, or safety measures.
Types of certificates of origin
There is no standardised certificate of origin (CO) form for global trade, since specific requirements vary depending on the type of goods and destination.
Certificates of origin are primarily divided into two types: non-preferential and preferential.
- Non-Preferential CO: Also known as an “ordinary CO”, this indicates that the goods are not eligible for reduced tariffs or tariff-free treatment under trade arrangements between countries. An ordinary CO is required if there is no treaty with the importing country or if a specific product is excluded from tariff relief.
- Preferential CO: This means that there is a free trade agreement or reduced tariffs in place between countries. For instance, exports between EU countries are exempt under the EU free trade agreement and would receive a preferential CO.
Below is the general structure of a certificate of origin:
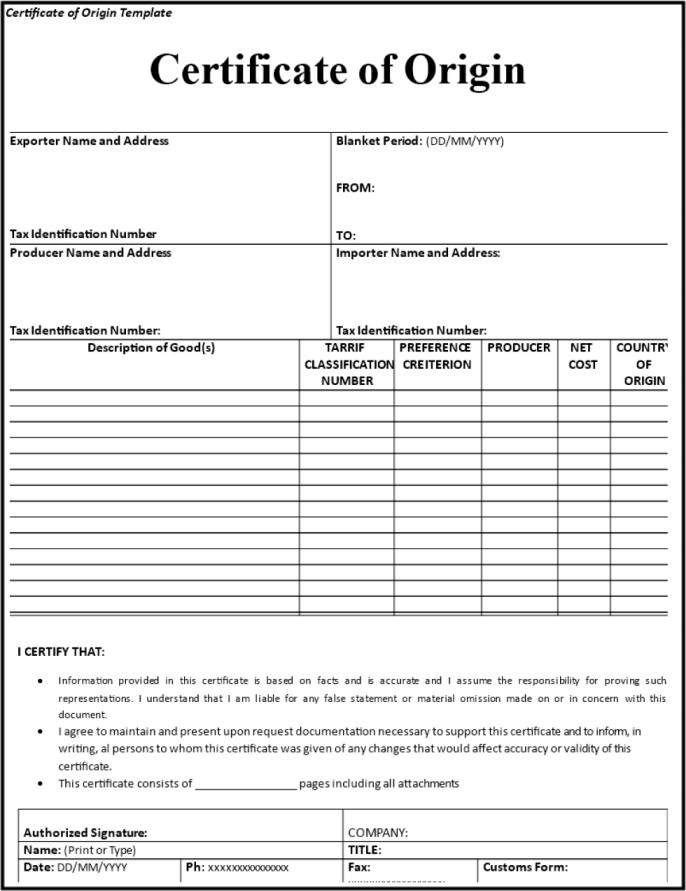
What is included on a certificate of origin?
The following information is usually included in COs:
- The name and contact details of the producer of the goods
- The name and contact details of the exporter
- The name and contact details of the importer/receiver
- The country of origin
- A clear goods description, including HS codes, quantity, size, and weight
- A waybill or bill of lading number
- Means of transport and route information
- Commercial invoice number(s) and date(s)
- Additional notes or remarks, if relevant
How to get a certificate of origin
The requirements for obtaining and validating a CO may vary depending on the country, but you will typically have to follow the steps below:
- Register as an exporter.
- Complete an appropriate affidavit.
- Provide a manufacturing or commercial invoice as proof of the origin of your goods.
- Fill out the certificate of origin.
- Submit a notarised affidavit and corresponding invoices, along with your CO, to your chamber of commerce, specifying which documents require stamping.
What is the customs procedure for validating a CO?
Customs officials at the border will examine the certificate of origin to determine the nationality of the goods. The authenticity of the document is verified by checking the:
- CO’s unique reference number
- Signatures on the document
- Validity of the CO (usually up to 12 months after the issue date)
- Official stamps
- Accuracy and consistency, particularly when compared to the commercial invoice and bill of lading
NEED MORE INFORMATION?
FAQ about the certificate of origin and commercial shipping
What determines the country of origin?
The country of origin is determined by various factors, including the parts or ingredients used, their sources, and the production process and location.
Do I need to provide a CO when shipping with Eurosender?
A certificate of origin is generally required for businesses shipping goods to non-EU countries, such as the UK. In many cases, the information contained in the CO may be included on the commercial invoice.
Can anyone produce their own certificate of origin?
No, certificates of origin must be issued by the chamber of commerce or a similar entity in the country of origin.
Can I use the same CO for another identical shipment?
No, certificates of origin are one-time documents, meaning each shipment requires a unique CO.
Can I get an electronic certificate of origin (eCO) instead of the normal paper CO?
The shipping industry is embracing technology and is likely to increase its use of electronic certificates of origin (eCOs) in the future. The WTO’s Trade Facilitation Agreement is supporting this shift towards electronic documentation.
- faster trading
- cost savings
- improved security
However, widespread adoption is currently limited due to the need for compatible platforms and processes. Check with your local chamber of commerce to determine whether this option is available. They can also provide information on any necessary steps that must be taken.